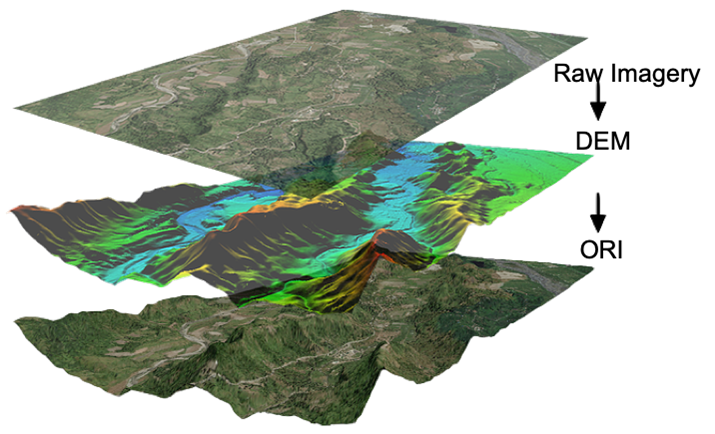
Technology Stack


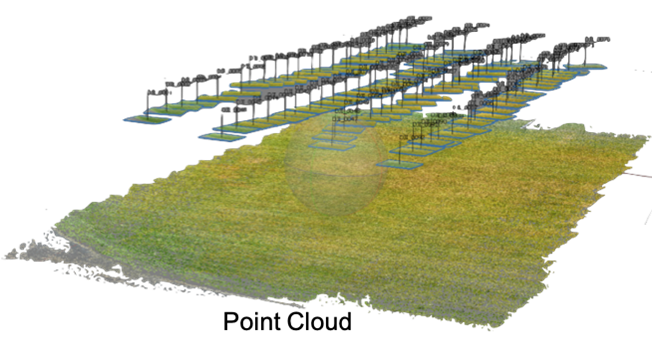
Technology Stack
At SAAR Geospatial, our solutions are powered by a robust and diverse technology stack, allowing us to deliver state-of-the-art GIS solutions, AI-driven data processing, and scalable web applications, tailored for diverse industry needs. Our expertise spans GIS dashboards, AI-driven data processing, and field surveys using the latest in geospatial and IT technologies.
Platforms:
1.A comprehensive GIS platform offering mapping, spatial analytics, and data visualization tools.
2.Ideal for creating interactive maps, conducting spatial analysis, and sharing insights across devices.
3.Widely used for urban planning, environmental management, and infrastructure projects.
Google Maps

1.A widely recognized platform offering rich mapping services and location data.
2.Features tools for route planning, geocoding, and interactive maps tailored to user needs.
3. Ideal for businesses needing location intelligence for logistics, delivery, or customer engagement.
Mapbox

1.A modern platform for creating highly interactive maps and visualizations.
2.Supports dynamic data rendering, including 3D maps, custom styles, and real-time updates.
3. Popular for applications like navigation, logistics, and retail location intelligence.
Google Earth Engine

1.A cloud-based platform for geospatial data analysis, processing, and visualization.
2. Provides access to petabytes of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets for large-scale environmental monitoring.
3. Frequently used in disaster management, deforestation tracking, and urban heat mapping.

1. An open-source GIS application known for its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem.
2. Enables advanced geospatial data editing, analysis, and visualization without licensing costs.
3. Perfect for customizing workflows and integrating with various spatial databases.




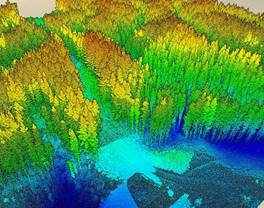
GIS Servers:
ArscGIS Server

1.A cloud-based platform for geospatial data analysis, processing, and visualization.
2. Provides access to petabytes of satellite imagery and geospatial datasets for large-scale environmental monitoring.
3. Frequently used in disaster management, deforestation tracking, and urban heat mapping.
GeoServer

An open-source GIS server, GeoServer is perfect for projects that demand flexibility and adherence to open standards.
Key Features
1.Supports multiple data formats, including shapefiles, GeoJSON, and PostGIS.
2.Implements open web services such as WMS, WFS, and WCS for data sharing.
3.Customizable with plugins and configurations to suit diverse project requirements
Mapping Libraries:
We utilize cutting-edge mapping libraries to deliver highly interactive, customizable, and responsive geospatial applications. These libraries form the backbone of our web mapping solutions, ensuring seamless data visualization and user engagement
OpenLayers
OpenLayers is a powerful open-source JavaScript library for building dynamic and interactive web maps.
Key Features
1.Supports multiple formats like WMS, WMTS, GeoJSON, and vector tiles.
2.Provides tools for styling, animations, and interactivity.
3.Compatible with major GIS servers such as ArcGIS Server and GeoServer.
4.Lightweight and flexible for custom map development
Why Use OpenLayers?
Ideal for projects requiring highly customizable and lightweight web mapping applications.
Leaflet.js
Leaflet.js is a leading open-source mapping library known for its simplicity, speed, and ease of use.
Key Features
1.Fast and lightweight, designed for mobile-friendly interactive maps.
2.Extensive plugin ecosystem for added functionality.
3.Supports GeoJSON and vector data visualization.
4.Compatible with popular mapping APIs like Google Maps and Mapbox.
Why Use Leaflet.js?
Perfect for creating intuitive and mobile-friendly mapping experiences.
Mapbox GL JS
Mapbox GL JS is a modern library for building highly interactive and visually stunning web maps.
Key Features
1.Provides dynamic, real-time rendering for vector and raster maps.
2.Fully customizable with 3D visualization and immersive user experiences.
3.Built-in support for integrating geospatial data from various sources.
4. High-performance rendering for seamless interaction with large datasets.
Why Use Mapbox GL JS?
Best suited for advanced projects requiring real-time updates, 3D maps, or custom styles.
Spatial Databases:
PostgreSQL (PostGIS)
PostgreSQL, combined with the PostGIS extension, is a leading open-source database for managing geospatial data.
Key Features
1.Advanced spatial functions, such as proximity searches, spatial joins, and intersection detection.
2.Support for 2D and 3D geospatial data with exceptional precision.
3.Seamless integration with tools like QGIS, GeoServer, and ArcGIS.
4.Scalable for handling large datasets across industries such as urban planning and environmental monitoring.
Why Use PostgreSQL (PostGIS)?
A reliable, open-source solution for comprehensive spatial data management and analysis.
Elasticsearch (Spatial Indexing)
Key Features
1. Fast spatial queries, including point, polygon, and distance-based searches.
2. Real-time visualization and analysis of geospatial data.
3. Compatible with mapping libraries like OpenLayers and Mapbox.
4. Scalable for large-scale and real-time applications like logistics and asset tracking.
Why Use Elasticsearch?
Ideal for projects needing rapid geospatial searches and analytics in real-time.
Oracle Spatial and Graph

Oracle Database provides enterprise-grade geospatial capabilities through its Spatial and Graph extension.
Key Features
1. Comprehensive support for vector, raster, and 3D geospatial data.
2. Built-in spatial indexing for efficient query performance.
3. Integration with Oracle’s analytics and cloud platforms.
4. Advanced geospatial functions for network analysis, geocoding, and topological processing.
Why Use Oracle Spatial and Graph?
Best suited for enterprise-level projects requiring robust, high-performance geospatial data management and analysis.
Microsoft SQL Server

SQL Server includes built-in spatial data support, enabling it to handle geospatial data effectively.
Key Features
1. Support for spatial data types like geometry and geography.
2. Integration with business intelligence tools for geospatial analytics.
3. Scalable and reliable for enterprise use cases.
4. Integration with ESRI’s ArcGIS and other GIS tools.
Why Use SQL Server?
Ideal for businesses already utilizing Microsoft’s ecosystem and requiring integrated geospatial capabilities.




Our Clients